Table of contents
No headings in the article.
What is DevOps?
It’s a cultural practice in an organization by the development team and operations team to use each other’s tool, to smooth out the process of software delivery.
DevOps aims: To resolve the issues in the development process that arise due to the conflicting goals and isolation of traditional development and operations teams.
DevOps Lifecycle:
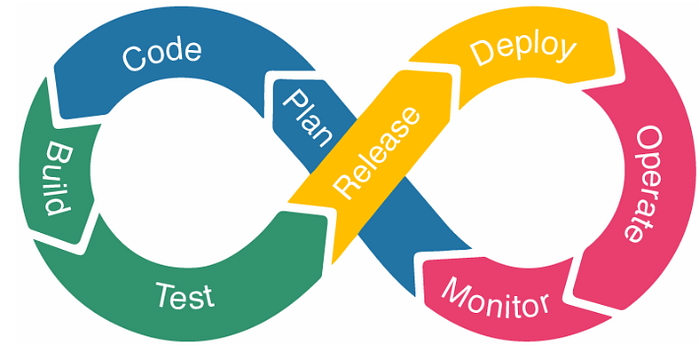
1. Plan — Professionals determine the commercial need and gather end-user opinions throughout this level. In this step, they design a project plan to optimize business impact and produce the intended result.
2. Code — During this point, the code is being developed. To simplify the design process, the developer team used version controls tools such as GIT, TFS, GitLab etc. that assist them in preventing safety problems and bad coding standards.
3. Build — After programmers have completed their task, they use tools such as Maven and Gradle to submit the code to the common code source.
4. Test — To assure software integrity, the product is first delivered to the test platform to execute various sorts of screening such as user acceptability testing, safety testing, integration checking, speed testing, and so on, utilizing tools such as JUnit, Selenium, etc.
5. Release — At this point, the build is prepared to be deployed in the operational environment.
6. Deploy — At this point, Infrastructure-as-Code assists in creating the operational infrastructure and subsequently publishes the build using various DevOps lifecycle tools.
7. Operate — This version is now convenient for users to utilize. With tools including Chef, the management department take care of server configuration and deployment at this point.
8. Monitor — The DevOps workflow is observed at this level depending on data gathered from consumer behavior, application efficiency, and other sources. The ability to observe the complete surroundings aids teams in identifying bottlenecks affecting the production and operations teams’ performance.
What is Automation, Scaling and Infrastructure?
Automation: Automate everything as much as possible and decrease the manual and repetitive work throughout the software development cycle. It boosts continuous integration. continuous delivery and continuous deployments.
Scaling: The ability to increase or decrease IT resources as needed to meet changing demand.
Infrastructure: The collection of hardware and software elements needed to enable cloud computing. It includes computing power, networking, and storage, as well as an interface for users to access their virtualized resources.
Why DevOps is Important?
DevOps describes a culture and set of processes that bring development and operations teams together to complete software development. It allows organizations to create and improve products at a faster pace than they can with traditional software development approaches
Here are the few reasons why devops is important
Shorter Development Cycles, Faster Innovation
Reduced Deployment Failures, Rollbacks, and Time to Recover
Improved Communication and Collaboration
It has more security